|
||||||||
 |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||
THE TORONTO CENTRE FOR PHENOGENOMICS
MOUSE IMAGING CENTRE |
 |
|
|
Optical Projection Tomography (OPT)Optical Projection Tomography (OPT) is an optical imaging tool that creates high resolution 3D images of samples that are over ten times larger than samples imaged with other optical microscopic techniques (1). OPT images also have excellent contrast between a fluorescent region of interest and the rest of the specimen. In OPT, a digital camera is used to capture an image of a transparent specimen. A specialized lens ensures that the image is formed only by the rays of light that are approximately parallel. This image is a projection through the specimen. A series of these projections obtained at various positions about the sample is used to create a 3-dimensional image of the sample. OPT is limited to transparent specimens as it is necessary to minimize light scattering through the sample. Mouse embryos are ideal specimens for OPT as they are naturally transparent. One of the great strengths of OPT is the ability to acquire fluorescent images. This allows a researcher to tie fluorescent molecules to a particular type of molecule, such as a type of protein or gene. OPT can be used to map the distribution of the fluorescent molecules, which is also a map of the distribution of molecule under study. At the Mouse Imaging Centre, we have begun research into altering the data processing methods in order to obtain higher resolution images of larger specimens. This will allow researchers to use OPT to study larger embryos and even complete organs.
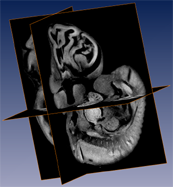
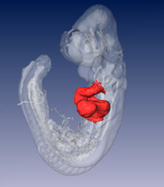
Above Left: Three orthogonal planes out of an autofluorescence OPT reconstruction of an E10.5 wildtype mouse embryo. The resolution of this image is approximately 20 microns. Above Right: Surface rendering of an E9.5 wildtype mouse embryo. Red: cardiac, white transparent: embryo.
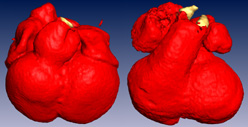
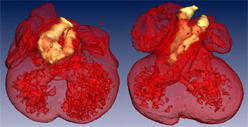
Above: Surface renderings of the cardiac region of E12.5 wildtype (left) and E12.5 Baf60c knockdown (right) mouse embryos. The outflow tract of the wildtype heart undergoes constriction and septation, whereas the outflow tract of the mutant has no constriction and little septation. Red: myocardium, yellow: interior vessels of great arteries. The myocardium is rendered transparently in the second set of images to easily see the interior of the great vessels. This work is described in "Baf60c is essential for function of BAF chromatin remodelling complexes in heart development" by H. Lickert et. al., Nature Volume 432, Nov 4 2004.
Design and Implementation of a Custom Built Optical Projection Tomography SystemA published blue-print of a custom OPT system is published here: A download package is available here (Update April 2014): OPT package **NOTE** All questions should be posed in our new forum http://optbuild.boards.net/
|
||||||
|
© 2004 The Centre for Phenogenomics |
|